Dark Matter - The Invisible Universe
What is dark matter?
Dark matter is a theoretical object that astrophysicist proposed to explain the discrepancy between well-study theory and observational data.
It only interacts with gravity and does not interact with the electromagnetic field, thus making it not absorb, emit, or reflect light. Our
current theory and measurements suggest that our universe is made of 5% matter, 26% dark matter, and 69% dark energy.
Observational Evidence for Dark Matter
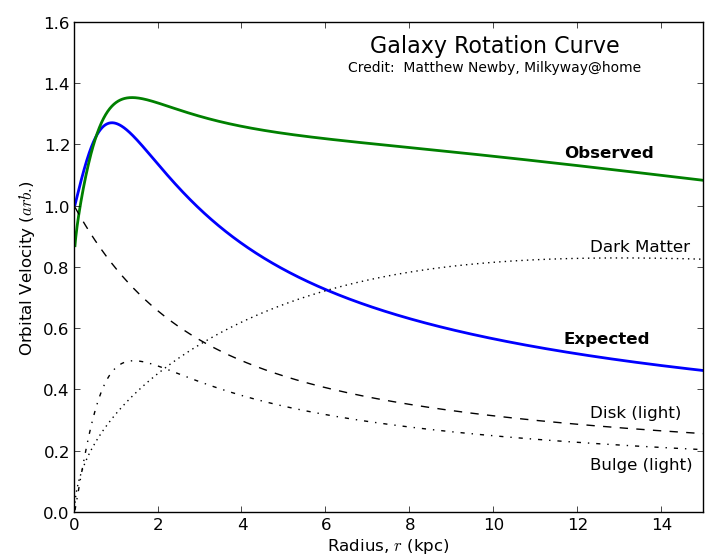
- Galaxy Rotation Curves
- The expected curve should follow an inverse squared law where the velocity drops as we go out in radius of the galaxy center.
- However, the observed galaxy rotational velocity stays constant as we increase in radius.
- Gravitational Lensing
- The bending of light from a distance galaxy right behind a huge cluster of invisible matter.
- This is also called an Einstein Ring.
- Click the image below to see more!

- The Cosmic Microwave Background
- The measured anisotropies CMB shows the density fluctuations in the early universe and they are consistent with dark matter model predictions.
- See more here.
Dark Matter Models
Dark Matter (DM) Model Properties
| Model |
Interaction |
Structure Formation Scale |
Candidates |
| Cold DM | slow, collisionless | cosmological scale | axions, WIMPs, MACHOs |
| Fuzzy Cold DM | extremely slow
(quantum wave motion) | smooths out small scale structures | ultra-light axions, WIMPs |
| Warm DM | intermediate speed | bottom-up | sterile neutrinos, gravitinos |
| Hot DM | ultra-relativistic | suppresses small scale structures | neutrinos |
| Self-interacting DM | slow | solves the cuspy halo problem | strong interaction particles |
| And many more! |
Open questions I am interested in:
- How do we interpret dark matter with quantum mechanics?
- When did dark matter form? What is its generator?
- What is its role during inflation?
- How do we solve small scale problems with our dark matter theories?
- Does dark matter decay over time?
- What is the unified theory?

